
|
I Introduction - Risks in Industry
The module includes three compulsory courses, covering risk management principles and risk analysis techniques in different industrial plants. The emphasis is on topics such as EU directives on industrial safety, major accident prevention, risk assessment methodologies applied to petrochemical and power industries, as well as environmental and human health hazards. The courses encompass the theoretical basics for rules and regulations, risk identification and analysis methods, on the other hand numerous examples demonstrate the milestones and recent events concerning industrial safety and security.
|
I-R01 INTRO: Introduction to Risk Management
The course covers the main topics of industrial safety, starting with different aspects of risks and terminology used in the field. The main part of the course is dedicated to the related EU directives and their application in industry. The course outlines goals, scope and required measures / obligations considering acute (e.g. accidents-related) and chronic (e.g. pollution-related) risks. Special attention is devoted to major accident prevention and related process safety risk assessment methodologies.
|

|
I-R02 PETRO: Risk Analysis in Petrochemical Industry
The petroleum industry is changing rapidly, challenging organizations and individuals to keep pace and distinguish opportunity from understanding, assessing and managing risk.
This course presents current global and regional issues of risk analysis in petrochemical industries.
Topics include risk aspects and methods for hazard identification, probability and consequences analysis, risk assessment, and health, safety and environment issues related to petrochemical industries.
|

|
I-R03 POWER: Risk Analysis in Power Industry
Knowledge of risk analysis applied specifically in power industry, starting with advantages and effectiveness of its application. It presents the regulatory basis and requirements, and elaborate commonly used methods through number of examples.
|

|
II Asset/Plant Oriented Risk Management
Three optional compulsory courses compose the second module. The asset and plant oriented risk management firstly introduces principles of Risk Based Inspection in petrochemical and power generation industries dealing with the most important risk-based approaches in line with the main standard documents, such as API RP 580 and API 581. The courses about RBI offer a state-of-the-art knowledge on methods and tools applied. Second, the module discusses methodologies for decision-making processes in maintenance and accident prevention. These are well illustrated by a number of instances from different industries.
|
II-R04a RBI-PETRO: Risk Based Inspection - Petro
The course elaborates on risk issues in petrochemical industries and explains principles of risk-based inspection. It deals with existing risk-based approaches and gives links to applied codes and standards. The focus of the course is on main reference documents of American Petroleum Institute: Recommended Practice for Risk-Based Inspection (API RP 580) and Base Resource Document on RBI (API Publication 581) API 581.
|

|
II-R04b RBI-POWER: Risk Based Inspection - Power
This course offers the state-of-the art knowledge of risk-based approaches currently applied in power generation industries. It highlights different levels of risk assessment and how to model consequences, as well as how to assess likelihood using statistical and other approaches. It goes deeper in risk sources including specific damage mechanisms commonly present in power plants. As an outcome, attendees will know how to optimize the inspection and monitoring strategy aimed to reduce risks and they will be able to optimize inspection plans and use inspection results in the risk management process of a power plant.
|

|
II-R05 RCM&RCFA: Reliability Centered Maintenance and Root Cause Failure Analysis
Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) and Root Cause Failure Analysis (RCFA) are methodologies used for logical decision-making process for analysis and definition of the equipment maintenance requirements, as well as for accident prevention. The focus of the course is on the damage mechanisms appearing in different industries. A large number of well elaborated examples is included.
|

|
|
The module concentrates on two main issues:
- The overview of EU regulation in the field of HSSE (Health, Safety, Security and Environment), explains the objectives and requirements, as well as the state-of-the art in the implementation including constraints and advantages. Special focus is on the Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control (IPPC) and Industrial Emission Directive (IED) and on the prevention of major accidents (Seveso); and
- General techniques for accident modeling and explains different models
of explosion. It elaborates gas and vapor explosion, as well as gas
dispersion modeling, using examples for applied methods. The course
includes modeling of fire and presents current models.
|
IIIA-R06 HSSE: Health, Safety, Security and Environment
The course gives an overview of EU regulation in the field of HSSE (Health, Safety, Security and Environment), explains the objectives and requirements, as well as the state-of-the art in the implementation including constraints and advantages. Special focus is on the Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control (IPPC) and Industrial Emission Directive (IED) and on the prevention of major accidents (Seveso).
|

|
IIIA-R07 CoF: Accident and Consequences Modeling
The course deals with accident and consequences modeling in industry. Three main topics are covered by the course: modeling of explosion, fire modeling and industrial fires. The modeling is elaborated by explaining general techniques and illustrated by examples of applied methods: CDF model, Baker-Strehlow-Tang model, Reynolds Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) model, as well as Phenomenological and Stoichiometric models. Attendees will not only be able to differentiate between fire and explosion, but also know how to do simple calculations of consequence with an appropriate comprehension of explosion mechanism and fire principles.
|

|
The module starts with the theory of fire and extinguishing, and thoroughly explains fire protection principles. Further, the course gives details related to the fire protection concepts including legal background and requirements with special focus on industrial fires and risk analysis. The course introduces basic principles and application of fire modeling, explains the phenomenon of a fire and gives an overview of the fire models and their hierarchy and discusses particular models, including numerical. The theoretical part is complemented with number of examples, including calculations, that illustrate the use of different fire models.
The EU directive ATEX is presented in details, along with the principles of explosion prevention and protection. Its practical application in the industrial plants is explained on a series of real life examples.
|
IIIB-R08 FIRE: Fire Protection
The course starts with the theory of fire and extinguishment, and thoroughly explains fire protection principles. Further, the course gives details related to the fire protection concepts including legal background and requirements with special focus on industrial fires and risk analysis. The course introduces basic principles and application of fire modeling, explains the phenomenon of a fire and gives an overview of the fire models and their hierarchy and discusses particular models, including numerical. The theoretical part is complemented with number of examples, including calculations, that illustrate the use of different fire models.
|

|
IIIB-R09 ExP: Explosion Protection
The EU directive ATEX is presented in details, along with the principles of explosion prevention and protection. Its practical application in the industrial plants is explained on a series of real life examples.
|

|
The module aims to explain the EU regulations in the field of safety and
health of workers at work. Main topics include general principles
concerning the prevention of occupational risks, the protection of
safety and health, the elimination of risk and accident factors, the
informing, consultation, balanced participation in accordance with
national laws and/or practices and training of workers and their
representatives, as well as general guidelines for the implementation of
these principles.
Principles of the EU regulation in the area of registration, evaluation and authorization of chemicals – REACH (EC Nr. 1907/2006). The course explains principles and obligations for manufacturers, importers and downstream users to ensure that they manufacture, place on the market or use such substances that do not adversely affect human health or the environment.
International and EU policies and legislative requirements related to
the transport of dangerous materials and explains the European Agreement
concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods. It elaborates
the main issues from ADR 2009 as well as safety measures and procedures
in case of accidents.
|
IIIC-R10 REACH: Risk Analysis of Chemicals
The course aims to explain principles of the EU regulation in the area of registration, evaluation and authorization of chemicals – REACH (EC Nr. 1907/2006). It gives an explanation of the principles and obligations for manufacturers, importers and downstream users to ensure that the manufacturing, placing on the market or the using of such substances do not adversely affect human health or the environment.
|

|
IIIC-R11 ADR: Transport of Dangerous Materials
The course covers international and EU policies and legislative requirements related to the transport of dangerous materials and explains the European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods. It elaborates the main issues from ADR 2013 as well as safety measures and procedures in case of accidents.
|

|
IIIC-R12 OSHA: Occupational Safety and Health
The course aims to explain the EU regulations in the field of safety and health of workers at work. Main topics include general principles concerning the prevention of occupational risks, the protection of safety and health, the elimination of risk and accident factors, general guidelines for the implementation of these principles as well as the the informing, consultation and balanced participation in accordance with national laws and/or practices. The course also discusses the training of workers and their representatives.
|

|
|
This module includes topics such as Risk governance concepts, Corporate social responsibility and sustainability, Emerging risks, Business communication and related topics. It gives an insight to the risks issues and complements other modules devoted mostly to the technical and engineering issues of risk management in industrial plants (petrochemical plants, process industry, power plants etc). In addition, it looks at the basic elements of the concept of Corporate (Social) Responsibility (CSR) and its practical application in industry. It starts with Key elements of the CSR, focuses on CSR methodologies and tools and on the technology related aspects as a part of the modern practices of industry (HSE, HSSE). Analysis/comparison of the practices in the EU, US and other countries and relevant data and information on best practices worldwide are elaborated, including a number of relevant case studies from the key industries and references to main sources of relevant
data and information. A particular unit of the course is dedicated to new ISO 260000 standard.
The modules continues with presentation of the principles of modern risk governance including its main elements (ef. IRGC framework): a) pre-assessment, b) risk appraisal, c) risk characterization and evaluation d) risk management and e-risk communication. Apart from each of the elements (e.g. under "Risk Assessment": hazard identification and estimation, exposure and vulnerability assessment, risk estimation, exposure and social concerns, socio-economic impacts) the examples from industrial practice will be shown and explained. A separate part is dedicated to the overview of specific methods and techniques (e.g. Delphi), as well as to the tools and instruments facilitating the application by industry, governments and public bodies.
Finally, the module highlights the topics related to emerging risks and introduces and transfers knowledge on emerging risks, and management of emerging risks. As "emerging" are considered primarily risks previously not recognized as risks, such as risks due to new processes, new technologies, new ways of working or social or organizational change (e.g. risks linked to nanotechnologies, bio-technology, new chemicals, outsourcing, globalization...). In addition the known risks emerging due to the change in public perception or new scientific knowledge are considered as well.
|
IVA-R14 iCSR&S: Integrated Corporate Social Responsibility and Sustainability
The course presents basic elements of the concept of Corporate (Social) Responsibility (CSR) and its practical application in industry. It starts with key elements of the CSR, focuses on CSR methodologies and tools and on the technology related aspects as a part of the modern practices of industry (HSE, HSSE). Analysis/comparison of the practices in the EU, US and other countries and relevant data and information on best practices worldwide are elaborated, including a number of relevant case studies from the key industries and references to main sources of relevant
data and information. A particular unit of the course is dedicated to the ISO 26000 standard.
|

|
IVA-R15 RGOV: Risk Governance
The course explains principles of modern risk governance including its main elements as described in the IRGC framework: a) pre-assessment, b) risk appraisal, c) risk characterization and evaluation d) risk management and e-risk communication. Apart from each of the elements (e.g. under "Risk Assessment": hazard identification and estimation, exposure and vulnerability assessment, risk estimation, exposure and social concerns, socio-economic impacts) the examples from industrial practice will be shown and explained. A separate part of the course will be dedicated to the overview of specific methods and techniques (e.g. Delphi), as well as to the tools and instruments facilitating the application by industry, governments and public bodies.
|

|
IVA-R17 EmRISK: Emerging Risks
The course introduces and transfers knowledge on emerging risks and management of emerging risks. The risks considered as "emerging" are primarily the risks previously not recognized as such, e.g. the risks due to new processes, new technologies, new ways of working or risks due to social or organizational changes (the risks linked to nanotechnologies, bio-technology, new chemicals, outsourcing, globalization are practical examples tackled within the course). The risks due to the change in public perception or new scientific knowledge are considered as well.
|

|
IVB Business sustainability
The modules complements other courses devoted to technical and engineering issues of risk management in industrial plants (petrochemical plants, process industry, power plants, etc.). Technical risks in the above plants can be a cause or a contributing factor in/for the business continuity and the final outcome of the technical/engineering activities is practically always to be seen on the background of business implications and implications/impacts to the business activities of a company. The insurance aspects are the most relevant practical aspect linking the engineering and business side of the company operation and asset management: therefore these will be tackled, too.
The module gives the participants opportunity to improve the knowledge about the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and to gain the skills to perform simplified LCA studies and to analyze, discuss and comment international scientific articles on LCA.
The course will provide a comprehensive overview of the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), Life Cycle Costing (LCC), International Reference Life Cycle Data System (ILCD) and European Reference Life Cycle Data System (ELCD). The focus will be on practical examples of applying LCA in industry and improving the environmental performance and sustainability of products and services.
|
IVB-R13 BUSINESS: Business Continuity Risks & Insurance
Complement other courses devoted to technical and engineering issues of risk management in industrial plants (petrochemical plants, process industry, power plants, etc.). Technical risks in the above plants can be a cause or a contributing factor in/for the business continuity and the final outcome of the technical/engineering activities is practically always to be seen on the background of business implications and implications/impacts to the business activities of a company. The insurance aspects are the most relevant practical aspect linking the engineering and business side of the company operation and asset management: therefore these will be tackled, too.
|

|
IVB-R16 LCA: Life Cycle Analysis and Assessment
The course gives the participants opportunity to improve the knowledge about the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and to gain the skills to perform simplified LCA studies and to analyze, discuss and comment international scientific articles on LCA.
The course provides a comprehensive overview of the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), Life Cycle Costing (LCC), International Reference Life Cycle Data System (ILCD) and European Reference Life Cycle Data System (ELCD). The focus will be on practical examples of applying LCA in industry and improving the environmental performance and sustainability of products and services.
|

|
IVC Risk management implementation
The Module covers:
- International Standard of ISO 31000:2009
elaborating the relationship between the risk management principles,
framework and process as described in this International Standard. The
course also highlights issues related to the applicability of the
standard in industry and in general.
- Cultural differences and multilingual issues playing an important role in the area of business communication which can easily fail on apparently banal issues. This could be of particular importance also in collaborative international projects.
- Management of innovation risks
The purpose of this course is to ensure that engineers, managers and IT experts can understand the importance of these aspects for the success of their collaboration with partners from other cultural background. It will address issues such as
- Intercultural value systems
- Differences in cultural practices
- Cross-cultural project management
- Individualism vs. Teamwork
- Successful management of cultural differences as a factor of success in international projects
- What one should know, do or not do in an EU project
- Case studies: US, Japan, India, China ...
In order to recognize, apprehend and manage cultural and international differences, a holistic and cognitive approach will be used throughout the training. This part of the module is designed for individuals and Small- and Medium-sized Enterprise interested in the topic.
The last part is devoted to the risk related to the development of new products and technologies. The success of the new technology does not lie just in the invention part or in the generation of innovative ideas, but in the successful management of the innovation process from an idea to products and services in the market. The management of innovation is a rigorous process which includes a disciplined, stage-by-stage approval process combined with regular measurement of every critical factor, ranging from the capability of the product to reach the target characteristics to success in the market.
|
IVC-R19 BC&M: Business Communication and Management of Intercultural Differences
In the times of ever increasing globalization, cultural differences and multilingual issues play an important role in the area of business communication which can easily fail on apparently banal issues. This could be of particular importance also in collaborative international projects. A cognitive approach toward cultural and national differences will be used throughout the training.
|

|
IVC-R32 ISO31000: ISO 31000 Principles and Management
The course covers the International Standard of ISO 31000:2009 highlighting the relationship between the risk management principles, framework and process as described in this International Standard. The course also highlights issues related to the applicability of the standard in industry and in general.
|

|
|
This module also offers topics related to the main topics of health oriented risk analysis with different aspects of risks and terminology used in the field. The main part of the course is dedicated to the related actions used in overall analysis (assessment, perception, communication etc.). Furthermore, the course is illustrated by a number of examples, presents commonly used methods, in particular the issues like (1) Basics of Risk: Analysis, Assessment and Management, (2) Risk Analysis in Perspective (Measures of Risk), (3) Dose-Response Functions, (4) Risk Perception and Communication, (5) Variability and Uncertainty, (6) Cumulative Risk Assessment, (7) Risk Assessment, Management and Law and (8) Application to Public Health- WHO Methodology. The second part of the module has focus on the standard of American Petroleum Institute API 581 (API RECOMMENDED PRACTICE 581:2008 Risk-Based Inspection Technology) and its application in petrochemical industry.
|
VA-R27 PubHealth: Public Health Oriented Risk Analysis
The course covers the main topics of health oriented risk analysis with different aspects of risks and terminology used in the field. The main part of the course is dedicated to the related actions used in overall analysis (assessment, perception, communication etc.). Furthermore, the course is illustrated by a number of examples, presents commonly used methods, in particular the issues like (1) Basics of Risk: Analysis, Assessment and Management, (2) Risk Analysis in Perspective (Measures of Risk), (3) Dose-Response Functions, (4) Risk Perception and Communication, (5) Variability and Uncertainty, (6) Cumulative Risk Assessment, (7) Risk Assessment, Management and Law and (8) Application to Public Health- WHO Methodology.
|

|
VA-R28 RBICon: API RBI Concepts in Industry
The focus of the course is set on the standard of American Petroleum Institute API 581 (API RECOMMENDED PRACTICE 581:2008 Risk-Based Inspection Technology) and its application in petrochemical industry. The course elaborates the basic concepts of API 581 and explains the principles of Risk Based Inspection. This methodology encompasses techniques such as Probability of failure, Consequence of failure, Risk analysis and Inspection planning based on Risk Analysis.
|

|
VA-R29 P&C: Probability and Consequence of Failure of Equipment
The focus of the course is given to the RBI approach to the inspection planning in petrochemical industry as defined by the standard of American Petroleum Institute API RECOMMENDED PRACTICE 581:2008 Risk-Based Inspection Technology (API 581).
The course provides quantitative procedures to establish an inspection program for pressurized fixed equipment by using risk-based methods. The procedure includes calculation of probability and consequence of failure, risk analysis and inspection planning based on the assessed risk. The pressurized fixed equipments covered by this course are pressure vessels, piping, tankage, pressure relief devices and heat exchanger tube bundles.
|

|
|
This module is devoted to the advanced issues of RBI analysis and, in particular, to the analysis of consequences of failure as defined by API RP 581:2008 Risk-Based Inspection Technology. It starts with general definitions aiming to ensure better understanding of the main topics of the module. The methodology for calculation is always illustrated with examples. The second part looks at the document CWA (CEN Workshop Agreement) 15740:2008, Risk-Based Inspection and Maintenance Procedures for European Industry (RIMAP). It explains the reasons to develop the European procedure and its differences and advantages in comparison to API RBI methodology. The focus of the last part of the module is on the damage mechanisms appearing in different industries and their influence to the calculation of probability of failure of equipment. A large number of elaborated examples are included.
|
VB-R30 CAA: Consequence Analysis in an API RBI Assessment
This course teaches how to calculate the consequence of failure as defined by API RP 581:2008 Risk-Based Inspection Technology. The course starts with general definitions aiming to ensure better understanding of the main topics of the course. Methodology for calculation is always illustrated with examples.
|

|
VB-R31 BasicRIMAP: CWA 15740 RIMAP - The Basics
The focus of the course is given to the document, CWA (CEN Workshop Agreement) 15740: 2008, Risk-Based Inspection and Maintenance Procedures for European Industry (RIMAP). It aims to explain reasons to develop the European procedure, differences and advantages in comparison to API RBI methodology.
|

|
VB-R33 RBI PoF: RBI Probability of Failure - Damage Factors
The focus of the course is on the damage mechanisms appearing in different industries and their influence to the calculation of probability of failure of equipment. A large number of well elaborated examples are included.
|

|
VC Special risk issues I.
This first part of the module presents the basic theory for safety and reliability analysis. The starting point is definition and discussion of basic concepts related to reliability and risk analysis. Then qualitative techniques like functional analysis, FMECA and identification and evaluation of faults and hazards are introduced. The next step is to introduce familiar quantification techniques like reliability block diagrams, fault- and event tree analysis, and Markov methods. Special attention is paid to safety-critical systems (IEC 61508) where analysis of systems with common cause failures is important. The course ends with methods for estimation of failure rates and a survey of reliability data sources.
The second part of the module presents theoretical backgrounds and state-of-the-art research issues on perception and communication of risk. It aims to provide a solid basis for further developments of such work tasks by including theoretical achievements in the related fields, various examples from field work, and an internal training exercise. The understanding of communication processes and the improving of information and communication techniques related to risk and hazards are central themes of the course. The course will also provide insight into selected historical aspects as well as current topics and literature. Lecturing is complemented with exercises based on experience of focus group work.
|
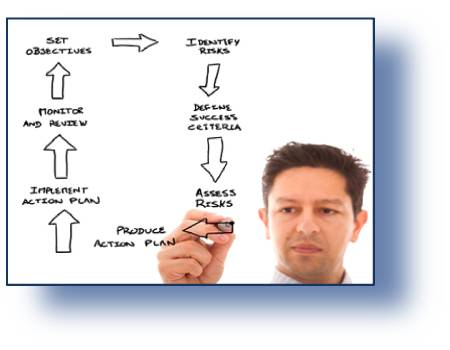
VC-R21 S&RA: Safety and Reliability Analysis
This course presents the basic theory for safety and reliability analysis. The starting point is definition and discussion of basic concepts related to reliability and risk analysis. Then qualitative techniques like functional analysis, FMECA and identification and evaluation of faults and hazards are introduced. The next step is to introduce familiar quantification techniques like reliability block diagrams, fault- and event tree analysis, and Markov methods. Special attention is paid to safety-critical systems (IEC 61508) where analysis of systems with common cause failures is important. The course ends with methods for estimation of failure rates and a survey of reliability data sources.
|
|
VC-R34 RP&C: Risk Perception and Risk Communication
This course presents theoretical backgrounds and state-of-the-art research issues on perception and communication of risk. It aims to provide a solid basis for further developments of such work tasks by including theoretical achievements in the related fields, various examples from field work, and an internal training exercise. The understanding of communication processes and the improving of information and communication techniques related to risk and hazards are central themes of the course. The course will also provide insight into selected historical aspects as well as current topics and literature.
In order to facilitate the bridge between theory and practice, a special attention will be given to two methodologies that enable the implementation of Risk Perception and Risk Communication concepts: The Delphi and the Focus Group. Beyond their description, this unit will be complemented with exercises based on experience of Focus & Delphi group work.
|

|
VD Quantitative Risk Assessment
The module presents an introduction to Quantitative Risk Analysis, thus illustrating the necessary steps for the calculation of risk indexes.Practical approach to frequency calculation and consequence assessment, including vulnerability models, is discussed. A specific focus on domino effect and accidents triggered by Natural-Technological (Na-Tech) events is presented.
In the second part the aim of is the introduction to transportation risk analysis. The risk assessment of road, rail and pipeline transportation of hazardous substances is illustrated. The approaches to frequency calculation, consequence assessment and risk assessment is discussed. Case-studies are analyzed to illustrate the calculation and the use of individual, societal and other advanced risk indexes.
|
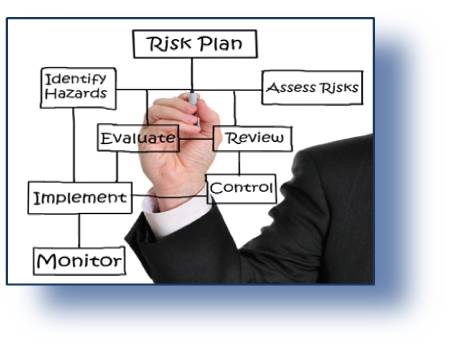
VD-R26 QRA&A: Quantitative Risk Assessment and Advanced Applications
The course presents an introduction to Quantitative Risk Analysis, thus illustrating the necessary steps for the calculation of risk indexes.
Practical approach to frequency calculation and consequence assessment, including vulnerability models, will be discussed. A specific focus on domino effect and accidents triggered by Natural-Technological (Na-Tech) events will be presented.
|
|
VD-R35 TRA: Transportation Risk Assessment
The aim of the course is the introduction to transportation risk analysis. The risk assessment of road, rail and pipeline transportation of hazardous substances will be illustrated. The approaches to frequency calculation, consequence assessment and risk assessment will be discussed. Case-studies will be analyzed to illustrate the calculation and the use of individual, societal and other advanced risk indexes.
|

|
VE Special risk issues II.
The module cover two main topics:
-
Vulnerability Analysis as a prerequisite to a risk assessment. Coupled with return on prevention analysis it could serve as an essential step in risk management and future scenarios development, giving managers and risk specialists a powerful decision assisting tool. This course aims to build up competences regarding vulnerability analysis in industry based on the current best practice in EU, as well as to provide basic knowledge regarding Return on Prevention Vulnerability analysis. Return on Prevention assessment gives the efficiency of the money and resources invested. The course presents the latest methodologies and instruments and also the latest stage of art.
- Industrial Risk Psychology as the scientific study of employees, workplaces, and organizational risks. Industrial Risk Psychology (IRP) contributes
to an organization's success by improving the performance and
well-being of its people and technological process. An IRP psychologist
researches and identifies how risks can improve behaviors and attitudes
by using risks through hiring practices, training programs, and feedback
systems. IRP psychologists also help organizations' transition among
periods of change and development.
|
VE-R37 VA&PA: Vulnerability Analysis and Return on Prevention Analysis
Vulnerability Analysis is a prerequisite to a risk assessment. Coupled with return on prevention analysis it could serve as an essential step in risk management and future scenarios development, giving managers and risk specialists a powerful decision assisting tool. This course aims to build up competences regarding vulnerability analysis in industry based on the current best practice in EU, as well as to provide basic knowledge regarding Return on Prevention Vulnerability analysis. Return on Prevention assessment gives the efficiency of the money and resources invested. The course presents the latest methodologies and instruments and also the latest stage of art.
|
|
VE-R38 IRP: Industrial Risk Psychology
Industrial Risk Psychology is the scientific study of employees, workplaces, and organizational risks. Industrial Risk Psychology (IRP) contributes to an organization's success by improving the performance and well-being of its people and technological process. An IRP psychologist researches and identifies how risks can improve behaviors and attitudes by using risks through hiring practices, training programs, and feedback systems. IRP psychologists also help organizations' transition among periods of change and development.
|

|
VF Special risk issues III.
The module looks at two main issues:
- Decision making as a process where multiple factors interact to shape the final outcome. Those factors can be technical, informational, emotional/psychological, cultural… Nevertheless, the limited rationality of economic operators makes the decision exercise more and more difficult in a more and more complex world. Safety management requires short, mid and long term decisions that may highly influence the ability of the organization to cope with its risks.
- The Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) as used in the safety and risk assessment, in particular for assessing and managing emerging risks linked to New Technologies.
Main concepts developed by organizations like OECD, API, HSE/HSL, CCPS or VCI are presented in detail. Application of these and other concepts, as well as the corresponding guidelines, are discussed in the second part of the course, where also the practical aspects of these applications, including tools and practical views from industry on the use of indicators are presented and discussed.
|
VF-R39 DAA: Decision Aid Approaches for Risk Management
Decision making is a process where multiple factors interact to shape the final outcome. Those factors can be technical, informational, emotional/psychological, cultural… Nevertheless, the limited rationality of economic operators makes the decision exercise more and more difficult in a more and more complex world. Safety management requires short, mid and long term decisions that may highly influence the ability of the organization to cope with its risks.
|

|
VF-R40 KPI: Concepts and Applications of Key Performance Indicators for New Technologies
The course addresses the issue of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) as used in the safety and risk assessment, in particular for assessing and managing emerging risks linked to New Technologies.
Main concepts developed by organizations like OECD, API, HSE/HSL, CCPS or VCI are presented in detail. Application of these and other concepts, as well as the corresponding guidelines, are discussed in the second part of the course, where also the practical aspects of these applications, including tools and practical views from industry on the use of indicators are presented and discussed.
|

|
|
|